RESISTOR PROPERTIES, COLOR CODE CHART AND CALCULATOR |
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
<-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
Everyone who has ever dealt with the circuits knows about the resistor. Here I will try to give you a bit deeper insight into this component. For those new to electronics, resistor is a two-terminal component used in electronic circuits to limit the flow of an electric current. I'll start with a brief introduction to its lesser understood physical meaning. In general, if the current flow "i" through an object inserted in a circuit is directly proportional to the voltage "V" across it, the ratio of "V" divided by "i" will be constant. This constant ratio is called resistance: R=V/i. In an ideal resistor R does not depend on the current over a considerable range of conditions. If by definition R=V/i, then i=V/R. This relationship is referred to as Ohm's law. |
|
|
Free JavaScripts provided
by The JavaScript Source |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
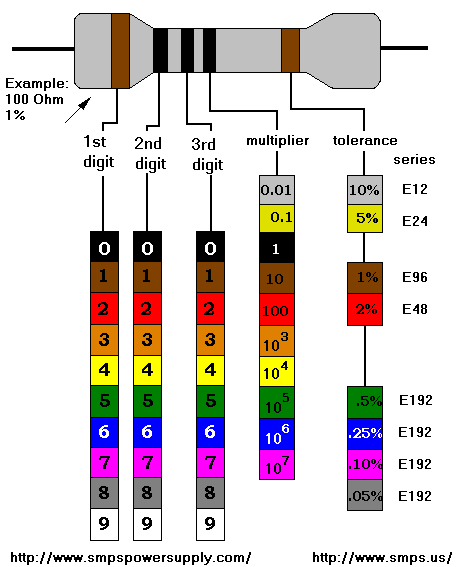
Note that only certain "standard" component values specified by Electronic Industries Association (EIA) and IEC publication 60063 may actually be available. See a complete printable standard decade resistor values table. Note that resistors may have different number of color bands depending on the tolerance. Below is an example of a 5 band color code. The same color scheme is used for small capacitors (in picofarads pF) and inductors (in microhenries µH), although they often have the numeric values actually stamped on them. Also see electrical formulas for series and parallel connections. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
<------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------> |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lazar Rozenblat

